Body Interventions refer to a wide range of image-guided, minimally invasive procedures that target diseases affecting internal organs and blood vessels.
- Ambawadi, Ahmedabad 380006
- +91 85116 41339
Body Interventions

Body Interventions
- These techniques allow for precise treatment without the need for open surgery—resulting in faster recovery, fewer complications, and shorter hospital stays.
Conditions We Specialize In Treating
Our comprehensive approach covers a broad spectrum of neurovascular conditions, ensuring targeted and effective interventions.
- ✓ Image-Guided Biopsy & Drainage
- ✓ Hemoptysis – Bronchial & Pulmonary Artery Embolisation
- ✓ Gastrointestinal Bleeding – Embolisation
- ✓ Vascular Malformation – Embolisation & Sclerotherapy
- ✓ Prostatic Artery Embolisation for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Our Streamlined Treatment Process
- 1. Initial clinical assessment
- 2. Diagnostic imaging (Ultrasound/CT/MRI)
- 3. Procedure planning
- 4. Image-guided intervention under local anesthesia or mild sedation
- 5. Monitoring & follow-up care
Interventions: Pros & Cons
| Advantages (Pros) | Considerations (Cons) |
|---|---|
| Minimally invasive | Needs imaging and skilled radiologist |
| Less pain and shorter hospital stay | May not be suitable for all patients |
| No general anesthesia required | Possibility of needing repeat procedures |
| Can treat multiple conditions effectively | Slight risk of bleeding/infection (very rare) |
Results & Recovery Journey
- 💪 Thrombectomy: Immediate neurological improvement often observed if performed within the critical window.
- 🏠 Stenting & Embolisation: Most patients are discharged within 2–3 days, with a focus on rapid and comfortable recovery.
- 📈 Long-term results: Durable outcomes are ensured through regular follow-up imaging and ongoing patient care.
Vital Patient Education
“Early intervention can save your brain. If you or a loved one experiences sudden weakness, speech difficulty, or vision loss — seek immediate medical attention. In stroke care, every minute counts.”
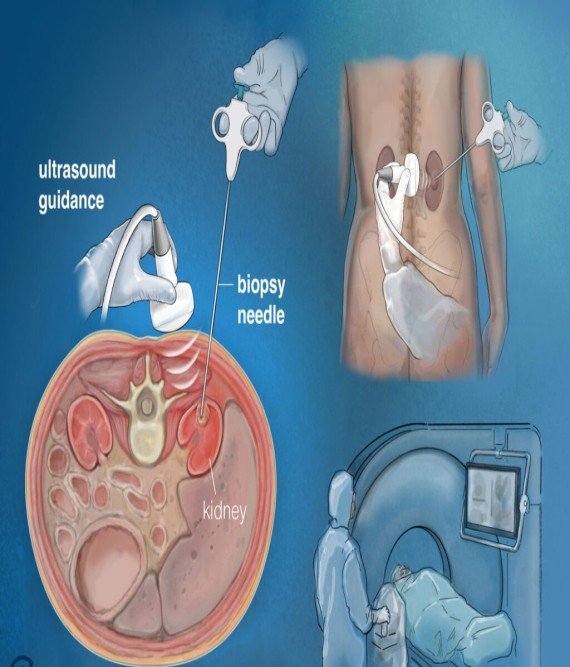
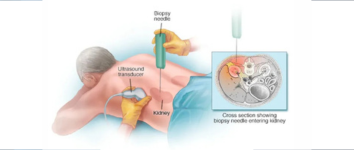
Image-Guided Biopsy & Drainage
What is it?
Minimally invasive procedures using imaging (like ultrasound or CT scans) to accurately guide needles for tissue sampling (biopsy) or to drain fluid collections such as abscesses.
Symptoms Indicating Need:
- • Suspicious lumps or masses
- • Unexplained infections
- • Persistent fluid collections
Treatment Approach:
Under imaging guidance, a needle is precisely inserted to collect tissue samples or drain fluids, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
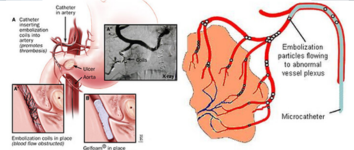
Hemoptysis – Bronchial & Pulmonary Artery Embolisation
What is it?
A life-saving procedure to control significant bleeding in the lungs by blocking the bleeding vessels.
Symptoms:
- • Coughing up blood
- • Shortness of breath
- • Chest discomfort
Treatment Approach:
Through a catheter, embolic agents are delivered to the bleeding vessels to stop the hemorrhage, stabilizing the patient.
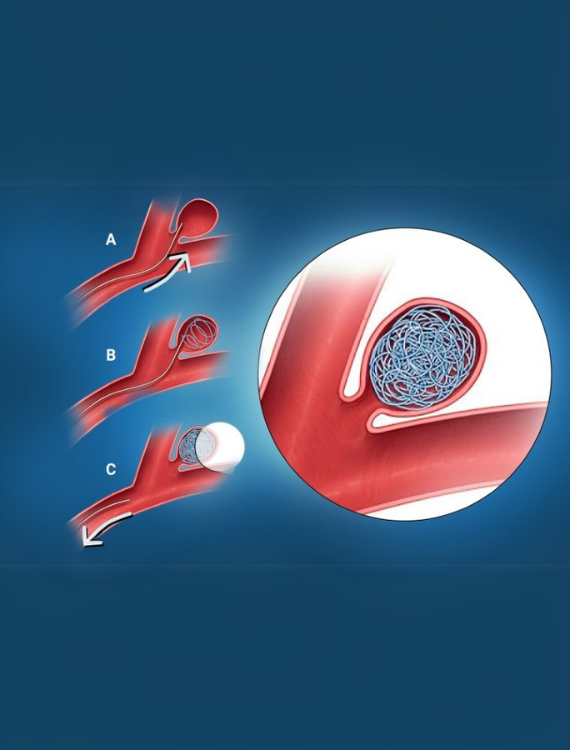
Gastrointestinal Bleeding – Embolisation
What is it?
A procedure to stop bleeding within the gastrointestinal tract by blocking the responsible blood vessels.
Symptoms:
- • Blood in vomit or stool
- • Black or tarry stools
- • Abdominal pain
- • Dizziness or fainting
Treatment Approach:
Using imaging guidance, a catheter delivers materials to occlude the bleeding vessel, effectively halting the hemorrhage.
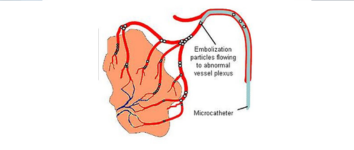
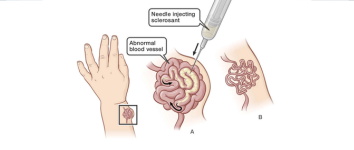
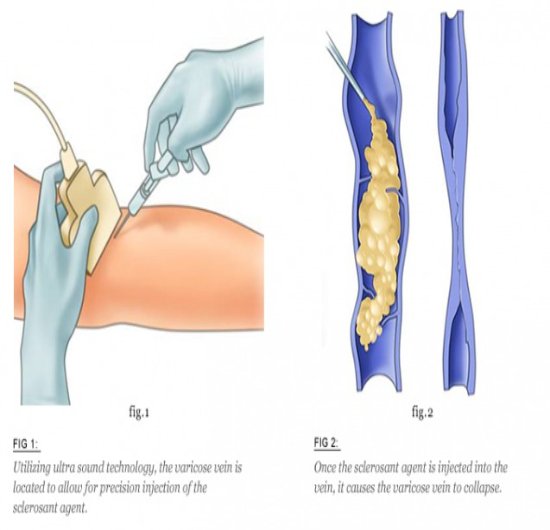
Vascular Malformation – Embolisation & Sclerotherapy
What is it?
Non-surgical treatments for abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can cause pain, swelling, or bleeding.
Symptoms:
- • Visible skin discoloration
- • Swelling or pain in affected area
- • Bleeding or ulceration
Treatment Approach:
Embolisation involves blocking abnormal vessels, while sclerotherapy uses a solution to shrink them, both aiming to alleviate symptoms.
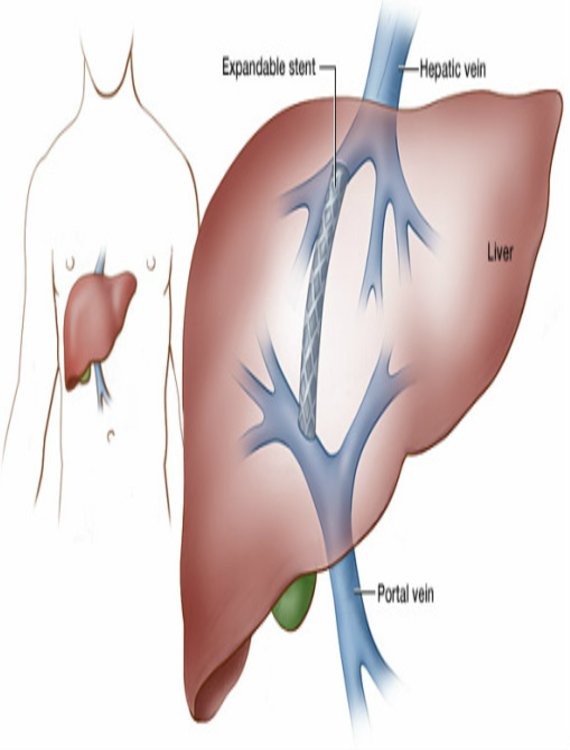
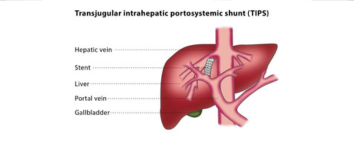
Liver Interventions – TACE, TIPSS for Portal Hypertension
What is it?
Advanced procedures to treat liver tumors and manage complications of portal hypertension.
Symptoms:
- • Abdominal swelling (ascites)
- • Variceal bleeding
- • Liver dysfunction
Treatment Approach:
- • TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization): Delivers chemotherapy directly to liver tumors.
- • TIPSS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt): Creates a pathway in the liver to reduce portal vein pressure.
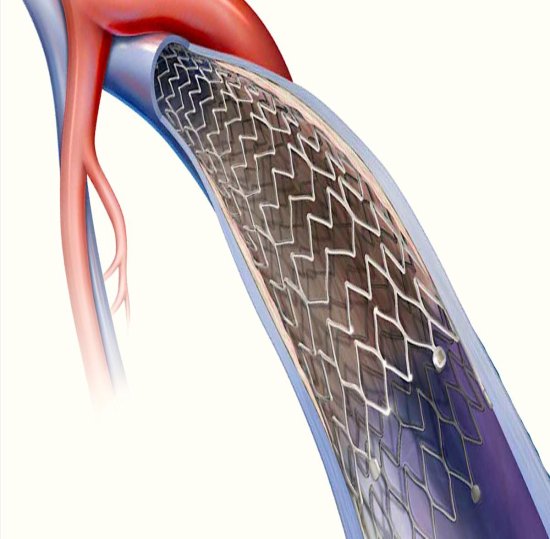
Vein Stenting | DIPS | PTBD
What is it?
Procedures to restore proper blood flow or bile drainage in cases of vein or bile duct obstructions.
Symptoms:
- • Leg swelling or pain
- • Jaundice
- • Abdominal discomfort
Treatment Approach:
- • Vein Stenting: Places a stent to open narrowed veins.
- • DIPS (Direct Intrahepatic Portocaval Shunt): Creates a channel in the liver to reduce pressure.
- • PTBD (Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage): Drains bile in cases of obstruction.
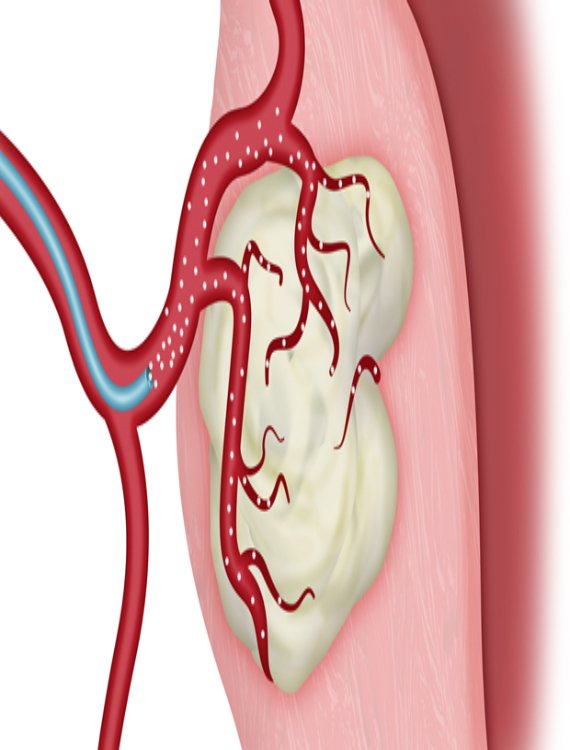
Uterine Artery Embolisation for Fibroid / PPH / Uterine AVM
What is it?
A minimally invasive treatment to address uterine fibroids, postpartum hemorrhage, or arteriovenous malformations by blocking blood flow to problematic areas.
Symptoms:
- • Heavy menstrual bleeding
- • Pelvic pain/li>
- • Postpartum bleeding
Treatment Approach:
Embolic agents are introduced via catheter to occlude specific uterine arteries, reducing symptoms and preserving the uterus.
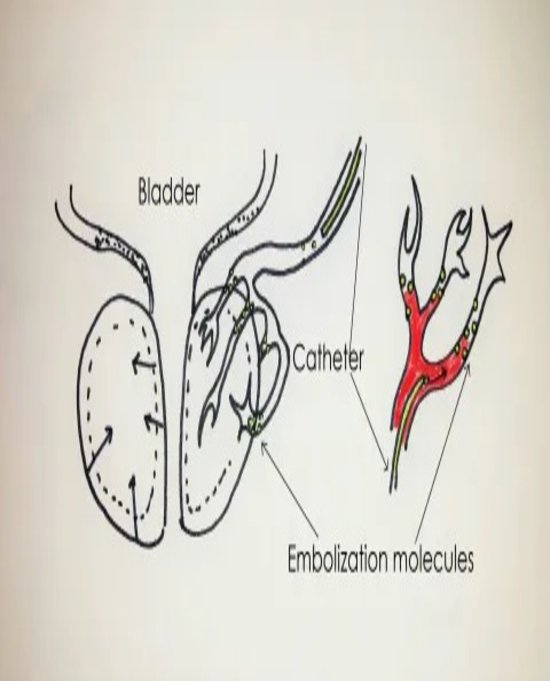
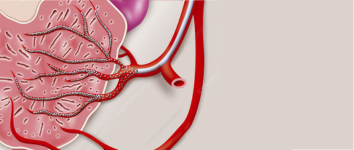
Prostatic Artery Embolisation for BPH
What is it?
A non-surgical procedure to alleviate urinary symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Symptoms:
- • Frequent urination
- • Weak urine stream
- • Incomplete bladder emptying
Treatment Approach:
Embolisation of prostatic arteries reduces blood flow, leading to shrinkage of the prostate and symptom relief.