Neurovascular interventions are advanced, minimally invasive procedures used to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the blood vessels of the brain and spinal cord. These treatments can be life-saving in emergencies like strokes or ruptured aneurysms, and can also improve long-term brain health by preventing future risks.
- Ambawadi, Ahmedabad 380006
- +91 85116 41339
Neuro Vascular Interventions

Advanced Neurovascular Interventions
- Our center specializes in precision-based, catheter-guided interventions that reduce recovery time, minimize surgical risk, and offer optimal outcomes for complex neurological conditions.
Conditions We Specialize In Treating
Our comprehensive approach covers a broad spectrum of neurovascular conditions, ensuring targeted and effective interventions.
- ✓ Ischemic Stroke (Blocked brain artery)
- ✓ Carotid Artery Stenosis
- ✓ Brain Aneurysms
- ✓ Brain AVM (Arteriovenous Malformation)
- ✓ Dural AVF (Dural Arteriovenous Fistula)
- ✓ Spinal AVM
Our Streamlined Treatment Process
- 1. Consultation & Advanced Imaging (MRI/MRA/DSA)
- 2. Precise Diagnosis & Personalized Treatment Planning
- 3. Minimally Invasive Procedure in a State-of-the-Art Cath Lab
- 4. Dedicated Post-Procedure Monitoring in ICU
- 5. Comprehensive Rehabilitation & Long-term Follow-up
Interventions: Pros & Cons
| Advantages (Pros) | Considerations (Cons) |
|---|---|
| Minimally invasive approach | May require follow-up imaging for monitoring |
| Significantly quicker recovery time | Not suitable for all aneurysm types or locations |
| Effectively prevents life-threatening events | Rare risk of vessel injury or re-bleeding post-procedure |
| Highly effective for elderly and high-risk patients | Requires a highly experienced and specialized medical team |
Results & Recovery Journey
- 💪 Thrombectomy: Immediate neurological improvement often observed if performed within the critical window.
- 🏠 Stenting & Embolisation: Most patients are discharged within 2–3 days, with a focus on rapid and comfortable recovery.
- 📈 Long-term results: Durable outcomes are ensured through regular follow-up imaging and ongoing patient care.
Vital Patient Education
“Early intervention can save your brain. If you or a loved one experiences sudden weakness, speech difficulty, or vision loss — seek immediate medical attention. In stroke care, every minute counts.”

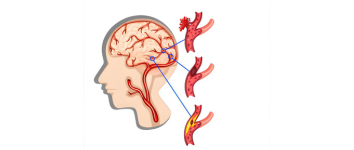
Stroke – Mechanical Thrombectomy
What is it?
Mechanical Thrombectomy is an advanced, minimally invasive procedure used to remove a blood clot from a blocked artery in the brain. It is primarily performed in cases of ischemic stroke, where a clot blocks blood flow to a part of the brain, leading to potential brain damage if not treated quickly.
Common Symptoms of Stroke:
- • Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side of the body)
- • Trouble speaking or understanding speechy
- • Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes
- • Dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination
- • Sudden severe headache with no known cause
How is it treated?
During a mechanical thrombectomy, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted through an artery (usually from the groin or wrist) and guided to the brain. A special device is used to grab and remove the clot, restoring blood flow. This procedure should ideally be done within a few hours of the stroke onset for the best outcome.
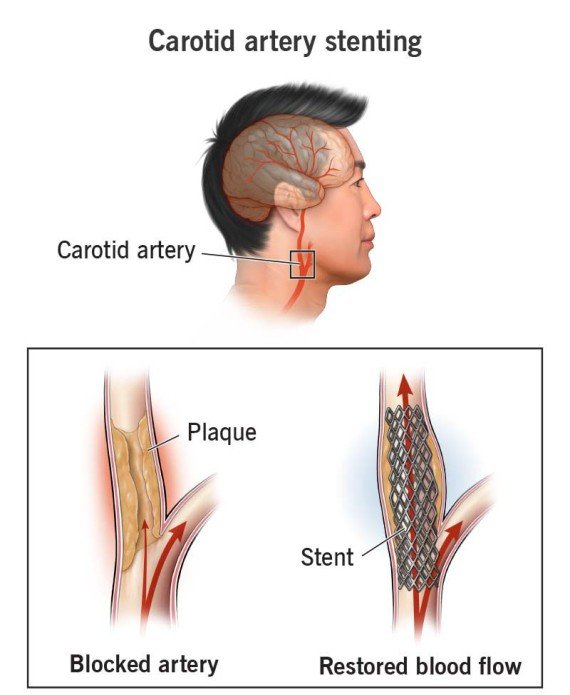
Carotid Artery Stenting
What is it?
Carotid Artery Stenting is a minimally invasive procedure used to open up narrowed or blocked carotid arteries — the main arteries in the neck that supply blood to the brain. Narrowing of these arteries (called carotid artery stenosis) increases the risk of stroke.
Common Symptoms (when present):
Carotid artery disease often has no symptoms until a stroke or mini-stroke (TIA) occurs. Warning signs may include:
- • Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- • Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- • Temporary vision loss in one eye
- • Dizziness or balance issues
How is it treated?
A catheter is inserted through the groin or wrist and guided to the carotid artery. A tiny balloon may be used to open the blockage, and then a stent (a small metal mesh tube) is placed to keep the artery open and ensure smooth blood flow to the brain.
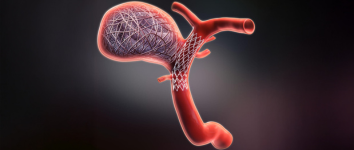
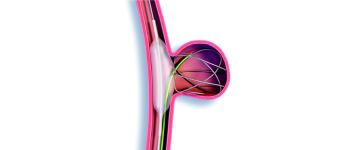
Brain Aneurysm – Simple Coiling
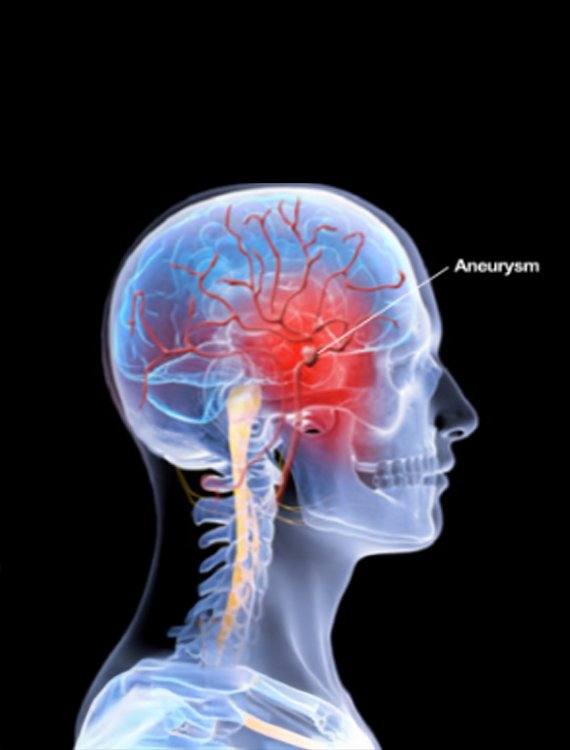
What is it?
Simple Coiling is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat a brain aneurysm — a weak, bulging area in a blood vessel in the brain that can rupture and cause bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). The goal of coiling is to seal off the aneurysm and prevent it from bursting.
Common Symptoms of a Brain Aneurysm:
- • Often no symptoms until it grows or ruptures
- • Headache or pain behind the eye
- • Vision changes or double vision
- • Difficulty concentrating or speaking (in large aneurysms)
How is it treated?
Through a small incision in the groin or wrist, a catheter is guided to the brain’s blood vessels. Tiny platinum coils are placed inside the aneurysm. These coils promote blood clotting inside the aneurysm, sealing it off from the rest of the bloodstream and preventing rupture.
Balloon Assisted Coiling
What is it?
Balloon Assisted Coiling is an advanced, minimally invasive technique used to treat complex or wide-necked brain aneurysms. It is a variation of simple coiling, where a small temporary balloon is used to help place coils securely inside the aneurysm without them slipping into the main artery.
When is it needed?
This method is typically used when the shape or size of the aneurysm makes regular coiling difficult. It helps stabilize the coils during placement and ensures the aneurysm is completely sealed off.
Common Symptoms of a Brain Aneurysm:
- • No symptoms in many cases until rupture
- • Localized headache or pain behind the eye
- • Blurred or double vision
- • Sudden severe headache (if ruptured)
How is it treated?
A catheter is inserted through the groin or wrist and guided to the brain. A small balloon is temporarily inflated across the neck of the aneurysm while the coils are placed. Once the coils are positioned properly, the balloon is deflated and removed.
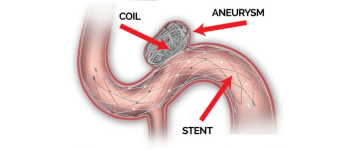
Stent Assisted Coiling
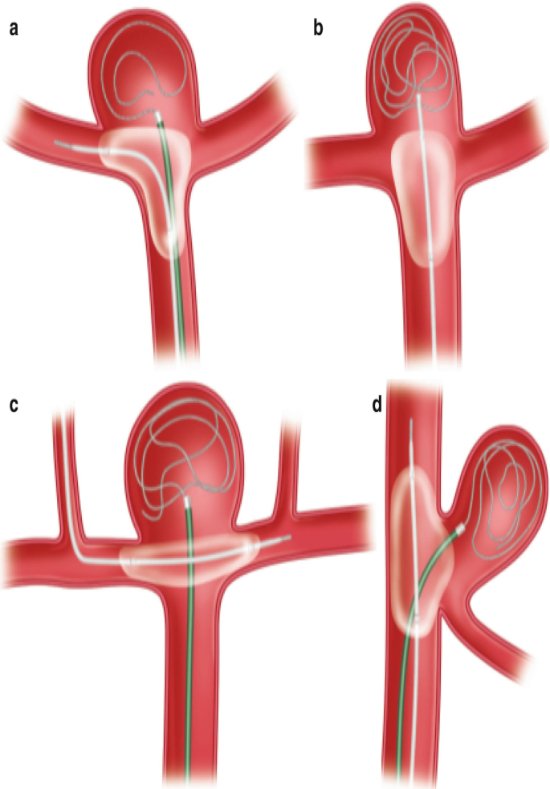
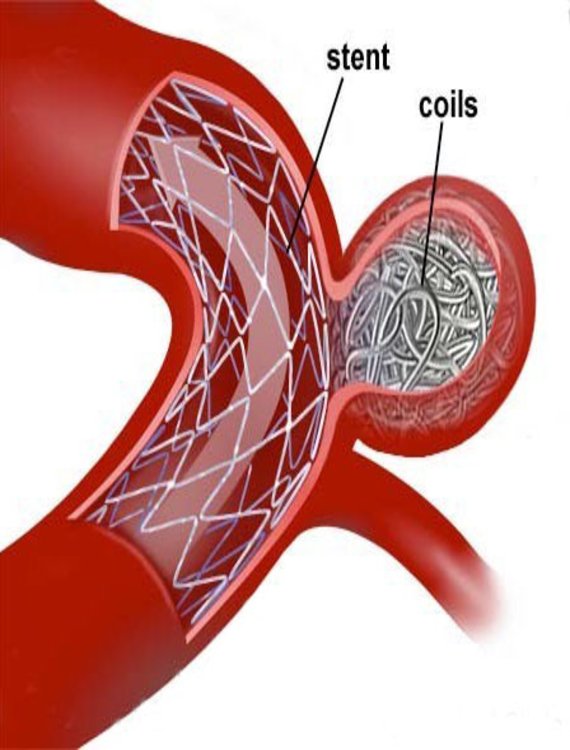
What is it?
Stent Assisted Coiling is an advanced, minimally invasive procedure used to treat wide-necked or complex brain aneurysms that cannot be safely treated with coiling alone. A stent (a tiny mesh tube) is placed inside the blood vessel to support the coils and keep them in place within the aneurysm.
When is it needed?
his technique is used when the aneurysm has a wide opening or is located in a position where coils might otherwise slip out. The stent provides a scaffold that allows safe and effective placement of the coils.
Symptoms of Brain Aneurysm
- • Often no symptoms until it ruptures
- • Headache or eye pain/li>
- • Vision changes
- • Sudden severe headache, nausea, or loss of consciousness (if ruptured)
How is it treated?
A catheter is inserted through the groin or wrist and navigated to the brain. First, a stent is deployed across the neck of the aneurysm. Then, through the stent, tiny coils are placed inside the aneurysm to block blood flow into it and prevent rupture.
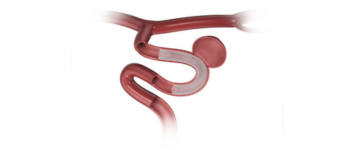
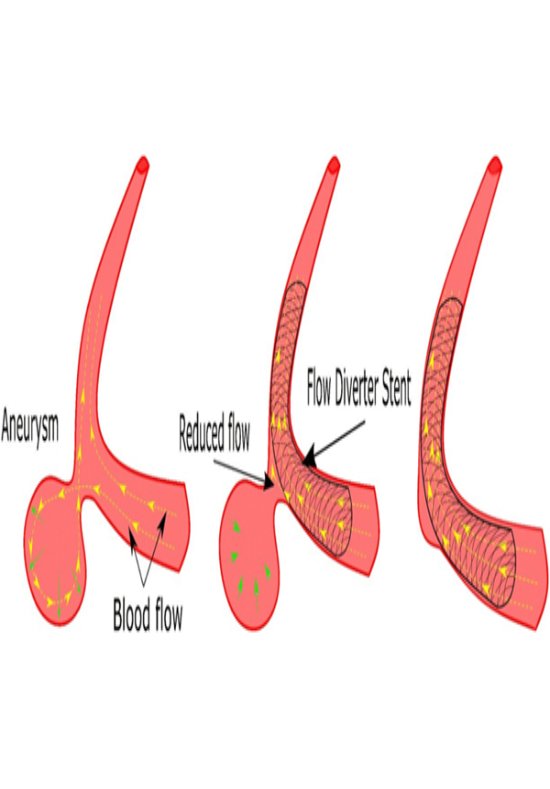
Flow Diverter
What is it?
A Flow Diverter is a special type of stent used to treat large, wide-necked, or complex brain aneurysms that are difficult to manage with traditional coiling techniques. Instead of filling the aneurysm, it redirects blood flow away from it, allowing the aneurysm to naturally shrink and heal over time.
When is it needed?
Flow diverters are ideal for large, giant, or fusiform aneurysms, especially those located in the internal carotid artery. They are used when other treatments like coiling or clipping are not suitable.
Common Symptoms of Aneurysm:
- • Often asymptomatic until rupture
- • Headache or eye pain
- • Vision disturbances
- • Sudden severe headache (if ruptured)
How is it treated?
A catheter is inserted through the groin or wrist and guided to the affected brain artery. The flow diverter stent is then placed across the opening of the aneurysm. This diverts blood flow away from the aneurysm, reducing pressure and promoting natural healing of the vessel wall.
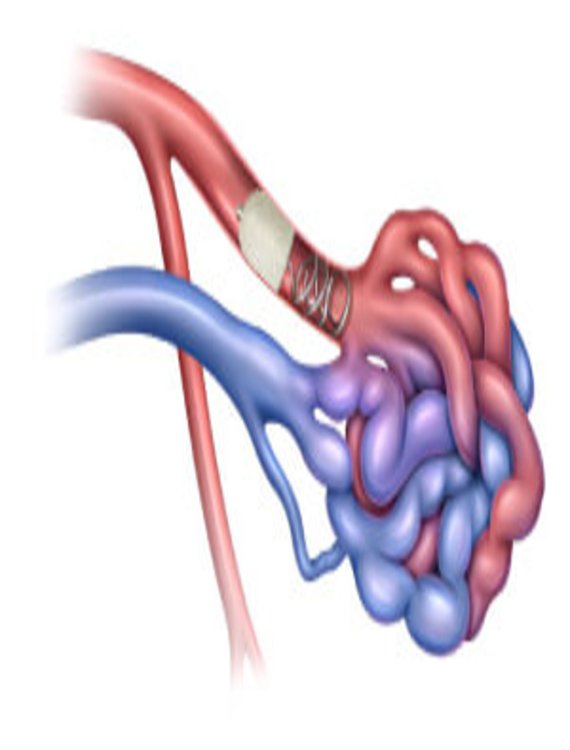
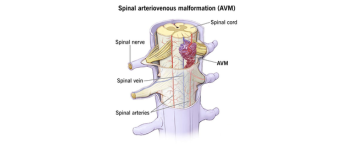
Brain AVM / Dural AVF / Spinal AVM – Embolisation
What is it?
Embolisation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat abnormal connections between blood vessels in the brain or spine. These include:
- • Brain AVM (Arteriovenous Malformation) – tangled vessels connecting arteries and veins
- • Dural AVF (Dural Arteriovenous Fistula) – abnormal connections in the lining of the brain
- • Spinal AVM – abnormal vessels in the spinal cord These conditions can cause bleeding, seizures, or neurological problems if left untreated.
Common Symptoms (vary depending on location):
- • Headaches or seizures
- • Sudden neurological changes (e.g., weakness, numbness, vision loss)
- • Back pain or limb weakness (in spinal AVM)
- • Hearing pulsating sound in the ear (in dural AVF)
- • Sudden bleeding in the brain (in severe cases)
How is it treated?
Using a catheter inserted through the groin or wrist, a special substance (such as medical glue or tiny particles) is injected into the abnormal vessels to block them. This reduces blood flow through the malformation, lowering the risk of rupture and improving symptoms.